Warehouse Management System.
Control and organize your warehouse.

The acquisition of a WMS needs to be well considered and is primarily a cost issue for companies. However, this is offset in the long term by the advantages of a warehouse management system.
Wanko offers the ideal application to control your logistics with its long-time proven WMS PraMag. PraMag not only supports its customers in terms of efficiency and optimization possibilities, but also stands out in daily practice due to its high acceptance by users.
PraMag - Advantages of the Warehouse Management System
- Cost reduction
due to fewer shortages
- Time saving
through optimized processes in the warehouse
- Increased inventory security
with better disposition possibilities
- Reduced excess inventories
single article
- Efficiency increase
through paperless picking
- Productivity increase
through foresighted warehouse planning
- More transparency
about the camp events
- Quality assurance
through complete documentation
- Optimal personnel planning
through better utilization of warehouse capacity
- Shorter training period
From employees
- Coordination of employees
in the warehouse by the control station
PraMag - Individual solutions for successful logistics.
Our strengths
- Industry and warehouse-independent software solution
- Part of a suite (WMS, TMS and FMS)
- Highly flexible through the use of workflows
- Fast customization options during ongoing operation
- Arbitrarily scalable
- Flexible implementation concept
- Uniform and understandable operation
Making complex structures and processes as simple as possible in practical application is part of our philosophy.
This also applies to the introduction of our software. It can be introduced completely at a specific point in time or gradually during ongoing operations.
Experts for the warehouse
Our project managers are your competent and reliable contacts during the implementation of our WMS in every phase of the project.
- Analysis of the actual processes
Joint consulting and concept development; creation of specifications (if necessary, also process description); - Employee training
on site and with us - Commissioning with competent support on site
- Consulting Service
during restructuring/reorientation, introduction of new processes, etc.
Additional options
- Individual report creation
- Key figure analysis
- Evaluations
- Multilingualism
Installing the files
Our files can be installed on popular devices
- MDEs
- Forklift terminals
- Smartphones
- Tablets
Thanks to a user-friendly interface and an understandable menu structure, employees quickly find their way around.
Barcodes
Our software is able to read all common barcodes. In practice, this saves employees time-consuming manual entries on the device.
Interfaces
- Connection to all common ERP systems
- Connection to SST from external service providers
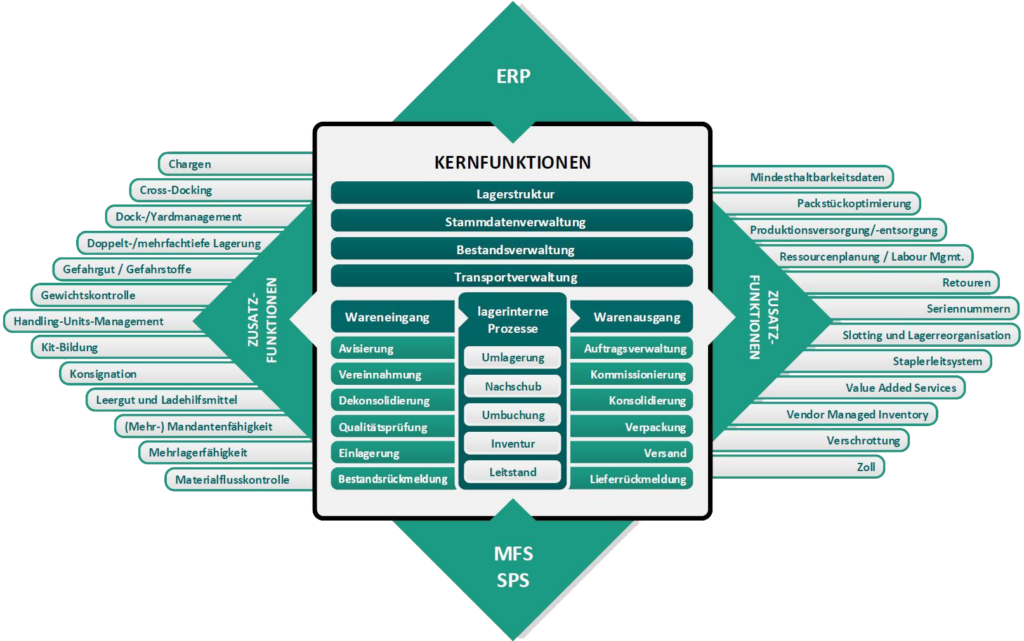
Core functions of a warehouse management system according to the guideline VDI 3601

Bearing structure
In order to replicate the diversity in the warehouse structure and thus guarantee its customers the best possible performance, PraMag uses various classification criteria:
- Zoning
The basic division into zones, e.g. goods receipt, collection zone, reserve zone, etc., allows a wide variety of process sequences to be mapped later. - Classification according to storage areas
To control the warehouse processes, the warehouse is divided into different storage areas. Storage, retrieval and picking areas are assigned per storage bin. - Aisle space compartment format
This enables a three-dimensional mapping of a storage location. The definition of the aisle-space-shelf format is essential for flexibility in warehouse conversions or expansions and decisive for orientation in the warehouse. - Storage bin attributes
Different attributes can be assigned to each storage bin (e.g. physical putaway block, occupied/not occupied, capacity and capacity monitoring, ABC area, etc.). - Warehouse modeling
The storage bins are created in the Inventory Information program. By assigning various attributes, the warehouse mirror is mapped according to the physical requirements and the intended optimizations in the warehouse.
PraMag can map any number of locations of a company. In doing so, each site can be organized according to its individual logical or physical organizational units, such as
- Bearing types
Pallet warehouse, high-bay warehouse, small parts warehouse, block warehouse, open-space warehouse - Storage areas
also warehouse subareas, storage bins, activity areas (work areas, transport areas, picking areas, and many more) can be configured.
Together with an easy-to-understand warehouse configuration and a high degree of adaptability (especially during live operation), we ensure the best possible site management and a high degree of practical everyday usability.
PraMag - Master data management in detail

Master data management
In master data management, the basic information that remains valid for a long period of time and that is relevant for the operation of a warehouse is mapped and maintained. Master data can apply to one site as well as to all sites.
All important master data objects such as customers, suppliers (clients, administrators), means of transport, branches and personnel can be managed in PraMag. In addition to data exchange via interfaces, it is also possible to create and maintain data independently of an interface.
Article master data
- Basic data
Article description, EAN, weight, dimensions, remaining shelf life, stock-separating characteristics such as MHD, batch, version, quota, etc. - Warehouse-specific (branch-related) data
Strategies, overdelivery tolerances, classification ABC areas, etc.
Means of transport master data
- Management of all common TM types
e.g. pallet, mesh box, container, tray, carton, corlette and many more incl. The dimensions - Account management
Load/unload customer, warehouse, forwarder, etc.
Subsidiaries
- Multi-storage capability, settings for residual quantity counting, etc.
Customer master data
- Customers
- Clients
- Administrator
- Warehouse
- Suppliers
User management
- User authorization
Assignment of an ID and individual permissions - Role management
Authorizations are granted via assignment to a role, facilitates the large-scale assignment of authorizations for a large number of employees.

Inventory management
Inventory management includes functionalities and methods for managing and finding the same as well as different inventory levels. With PraMag you master
- Inventory management accurate to storage location
- Inventory management according to stock-separating characteristics
Batch, best before date, version, quota, blocking indicator - Inventory management by inventory type
free, locked, quality locked - Use of strategies
Stock placement strategies, stock transfer strategies, stock removal strategies and stock reservation strategies based on a wide range of adjustable parameters - Booking history
All goods and TM movements within a warehouse can be tracked with a wide range of information - Warehousing
Chaotic warehousing (free choice of storage location by the system), warehousing with fixed locations - Printing of article labels and storage bin labels
- different storage options
Storage of article-clean or mixed load carriers - Digital stock mirror and path network
The so-called “route network double play” is used to optimize routes and avoid unnecessary trips.

Transport management
In PraMag, transport management is performed by
- Definition of forklift groups
Linking of forklift groups and work areas and storage of further parameters important for transport (full pallet transports, sequence/priority of work areas to be processed, etc.) - Definition of work areas
- Consideration of stage places
Transport from A to B via G
In PraMag we distinguish between
- Relocate
move a load carrier (LGT) from a source location to a destination location - Rearrange
Bring subset of an item from one LGT to another LGT

Goods receipt
Goods Receiving (GR) is the area where goods are physically received, inspected, recorded, and put away, making it one of the most important processes in a warehouse. It must be handled with great care, because any error will subsequently cause problems and unnecessary rework in one of the downstream warehouse processes. In PraMag, the process basically looks like this:
- Notification
Orders can be created and processed in PraMag either manually or automatically (if the data is transmitted via an SST from the upstream ERP system) - Order items
are created as payment advice stock (virtual stock) - Collection
The goods are received via scan with the MDE; actual stocks are compared against the advice stock and posted to a GR bin - Deconsolidation
If necessary, deconsolidation takes place before collection - Quality inspection
takes place according to the corresponding specification by the ERP system - Storage
the target search for storage is carried out on the basis of defined strategies and taking into account other parameters such as material groups (hazardous goods, heavy goods, etc.), permissible loading equipment types, storage zones, storage yard dimensions (including height assessment), etc. - Stock confirmation
Confirmation of the received goods to the ERP takes place
- Goods on consignment
Customer-related goods orders are marked separately by allocating a quota and are later taken into account in stock reservations. - Cross-docking processes
can be identified, managed and controlled by means of various parameters in the order / the goods. Complete storage of the goods is not required.

Outgoing goods
Goods issue is the area in which the goods to be delivered are physically removed from storage and booked out on the inventory side. In addition to the reservation / picking of goods, the goods issue process also includes the loading equipment registration as well as the control at staging or goods issue locations. In PraMag, the process basically looks like this:
- Order management
Orders can be created and processed in PraMag either manually or automatically (if they are transmitted via an SST from the upstream ERP system). - Order items
Based on the order items and taking into account existing stock-dividing characteristics (including quota goods), goods are reserved in the warehouse and
Picking tasks formed - Reservation of the stock
In the standard system, FIFO is used; FEFO is used for articles with an expiration date; LIFO can also be set. - Picking
The picking of the goods is done with the MDE and usually route-optimized (if necessary taking into account the weight or dangerous goods regulations, etc.). - Choice between guided picking and free picking
Collector is guided to the storage bin of the reserved goods / Collector decides independently from which storage bin he picks the goods - Destination search for parking
The destination search for picked goods is carried out on the basis of defined strategies and taking into account other parameters such as door specifications, specifications from the order (among others
Repacking specifications, existing packing stations, shipping stations for parcel services, etc.). - Consolidation
Optionally, goods can be consolidated/compacted in goods issue before loading - Packing
Printing of shipping labels and SSCC, delivery bills, freight documents - Shipping
After processing all tasks for a tour, loading takes place (taking into account the loading sequence) - Delivery confirmation
At the end of the tour, the picked goods and the empties used are reported back to the ERP.
Adjustable are
- Multi-level picking
- Block picking
- Order-, customer- or tour-related picking
- Consideration of full pallets and break-off quantity
- voucherless or voucher-based picking
- Override FIFO and FEFO if required

Internal warehouse processes
In the process of stock transfer, a load carrier (LGT) with goods is moved from a source bin to a new destination bin (planned stock transfer) on the basis of a transfer order (TO). LGT can also be run without existing TA (unplanned stock transfer).
- Stock transfer: planned/unplanned stock transfers
- Rearrange: subsets of an item are rearranged from a source LGT to a target LGT
- Return to storage: creation of transfer orders for clearing the collection zone
If a quantity of an item is required for picking, a stock transfer takes place in the form of a replenishment (from the reserve zone to the collection zone).
- planned (creation of TA on the basis of consumption values)
- Unplanned (by picker)
Quantity determination of replenishment e.g. from min./max. quantity; consideration of order quantities of open orders, etc.
A transfer posting changes at least one attribute of a position in the system. Permission to execute via appropriate permissions ensures unauthorized use of this option.
- Stock changes (attribute change, e.g. blocking indicator)
- Inventory corrections (quantity change) usually under specification of cost centers
A physical inventory is an inventory of all stock. In PraMag, each inventory is performed at the bin level. The places to be counted are grouped into tasks. The tasks are processed at the MDE, compared with the book inventory in the inventory program and, if necessary. Recounts created. A feedback to the ERP system is possible. Inventory in various forms (e.g. annual inventory, perpetual inventory) is supported. In PraMag, the process of an annual inventory basically looks like this
- Creation of an inventory incl. Inventory tasks
- Task processing at the MDE
- Control and reconciliation via inventory program
- Feedback to the ERP system
Other supported inventory types:
- permanent inventory
- Empty space count/empty space inventory
- Residual quantity count
- Stock changes (attribute change, e.g. blocking indicator)
- Inventory corrections (quantity change) usually under specification of cost centers
The control station provides an overview and tracking of all ongoing processes within the scope of picking, staging and loading. Various functions can be used to intervene in the operational processes.
- Display of all tours
Display of all tours of one day incl. Progress of picking, loading quantity, total weight, etc. - Priority control of the tours
- Representation of the individual orders
Orders of a tour, assigned pickers, used means of transport, current storage location, etc. - Possibility of manual intervention
in reservation, release picking, personnel deployment (collector allocation), shorten delivery order, process shortfall, transport control, etc. - Online notification
in case of shortages or stock differences, cancelled transfer orders or blocked storage bins - Communication with picker via message function
- Shipping document printing
Receipts, waybill, export documents and shipping labels
About configuration options are also available:
Delivery feedback to the ERP about the status in processes, e.g. in order picking
- Reservation made
- Picking started
- Goods provided
- Goods loaded
- Creation of an inventory incl. Inventory tasks
- Task processing at the MDE
- Control and reconciliation via inventory program
- Feedback to the ERP system
Other supported inventory types:
- permanent inventory
- Empty space count/empty space inventory
- Residual quantity count
- Stock changes (attribute change, e.g. blocking indicator)
- Inventory corrections (quantity change) usually under specification of cost centers
Additional functions of a warehouse management system according to the guideline VDI 3601
With the continuous management of batches from goods receipt to goods issue, detailed information and traceability is possible at any time in PraMag
- Batch management/batch tracing
- Stock separating feature during storage
- Blocking of stocks of certain batches
can be identified, managed and controlled by means of various parameters in the order / the goods. Complete storage of the goods is not required.
The storage and transportation of hazardous materials is not only physically challenging but also in terms of inventory management. PraMag is doing its part:
- Storage of article-specific dangerous goods information in the article master
- Storage control
Storage in special area and possibly dangerous goods relevant consideration of storage heights, storage together with other hazardous substances, etc. via strategies - Outsourcing control
Possibly prohibited combination with other articles/materials, special loading equipment/packaging for transport, etc. by restrictions and strategies.
Anyone can store, but proper storage needs to be learned and configured. In order to avoid hazards and potential causes of accidents, PraMag supports its users in the search for storage locations through
- Weight consideration
during storage in storage bins via weight restrictions - Control of bearing field and bearing compartment load
Consideration of the respective permissible total weight
In Wanko jargon, a handling unit (HU) corresponds to a load carrier (LGT). An LGT can contain goods or it can be an empty LGT in a storage bin.
- Management of all common load carriers
such as pallets, skeleton containers, totes, trays, cartons, corlettes, etc. including grouping options, account management (assignment of customer, forwarder, location, not subject to posting), deposit of dimension values - Hierarchical structure
through nesting of LGTs (“LGT on LGT”) - Identification and traceability of each LGT
by unique LGT number
- Clear identification of each individual loading aid
by assignment of a TM number - Management by means of loading accounts
- Calculation of capacities and volumes
by stored dimensions in the means of transport master
PraMag is used in a wide variety of industries, including the service industry. Here, goods from several clients must be managed in one storage location.
With PraMag you can
- Maintain data sets completely client-specific
concerns inventory data, supplier and customer data, user management, warehouse processes, allocation of storage areas and much more.
The branch functionality allows to manage spatially and organizationally separated warehouse locations and to configure them NL-specific. Relocations between the sites are realized through corresponding orders.
- Inventory overview per warehouse location / branch
- Stock overview as total stock
Control of transports, order processing, picking based on routines and configurable settings (e.g. priority control)
The management of goods subject to BBD is an important issue not only in the food industry but also in other sectors, e.g. in the building materials sector.
PraMag supports them in this with
- corresponding control of residual terms
- Consideration of residual terms
Within the framework of the availability check and stock reservation - Reservation according to FEFO
A separate production area within a warehouse requires the separate consideration and handling of the goods required from the goods required for delivery. Here, the WMS must not only take into account the required quantities for the end product, but also the transport to the designated storage area.
- Reservation and provision of quantities for production
Differentiation via versch. Item types in the order items - Production control station for the management of production orders
Overview of provided / missing goods; printout of production lists, quantity-dependent progress of production - Provision and feedback of finished productions
- Transport in loading zones via separate strategies
- Kit to Order
- Kit-to-Stock
In the case of returns, the first thing that matters is the direction of movement of the goods. If the goods return to the warehouse (customer return) or if the goods leave the warehouse (supplier return). The further process flows and control within the warehouse depend significantly on this.
Customer returns
are treated like goods receipts and can be extended by specifications in the order/order item to include a quality inspection, setting of a blocked stock characteristic and, if necessary, a quality check. Inventory adjustment postings (e.g. scrapping) are functionally extended
Supplier returns
are treated like goods issues, but can be executed independently of them through separate control (own reservation logic, allocation of a special picking area, etc.)
Empties returns
are – depending on the direction – treated like goods receipts or goods issues. Orders can be created manually or transmitted via the SST
Depending on the industry or certain product groups, serial number management makes sense or is required by law. Depending on the type of goods, complete tracking of the goods from the WE to the WA is required, or at least tracking at the WA is mandatory.
PraMag supports you with
- Capture of serial numbers during picking
Where-used list
A WMS should support the customer in optimizing his warehouse processes, especially in efficient warehouse utilization. This includes a well thought-out system for making the best possible use of the limited storage space available. PraMag offers you advantages here through
Automatic determination of a storage location
is carried out on the basis of storage strategies, taking into account a wide range of specifications such as
- Material data
e.g. dimensions (height rating) - ABC analysis
- Fixed place allocation
- Determination via WFL functionality
- Variable segments
e.g. in connection with cantilever racks or flexible storage in storage location segments
Automatic determination of a parking space
(for provisioning or for a replenishment) is done via appropriate strategies. Different parameters are taken into account, such as
- Specifications from the order
e.g. selection of the place on the basis of a shipping method - Characteristics of the order item on the picked LGT
e.g. printing of a special label
Based on defined parameters in the target search (height distance evaluation, aisle distribution, etc.), it is possible to check how the warehouse can be designed more optimally in terms of capacity utilization, route utilization, etc.
The occupation of valuable warehouse capacity by unsaleable goods is to be avoided, as is trouble with customers who have been supplied with them.
PraMag supports you with
- Separation of deliverable goods by means of blocking indicators
- Inventory correction of goods that are no longer saleable
per cost center posting for later traceability and feedback to the ERP - Return of goods no longer fit for sale
by supplier return (=return order)
Wanko customers are convinced and enthusiastic